Innovation is often defined as the creation of something new. Something fresh that hasn't been done before. In the competitive world of retail, that definition is expanded to include the word "quickly." The ability to innovate quickly without the risks frequently associated with experimentation is every retailer's dream, from the smallest specialty shops to big box retail. So innovation becomes less about creating something new and more about differentiating from the competition as quickly as possible.
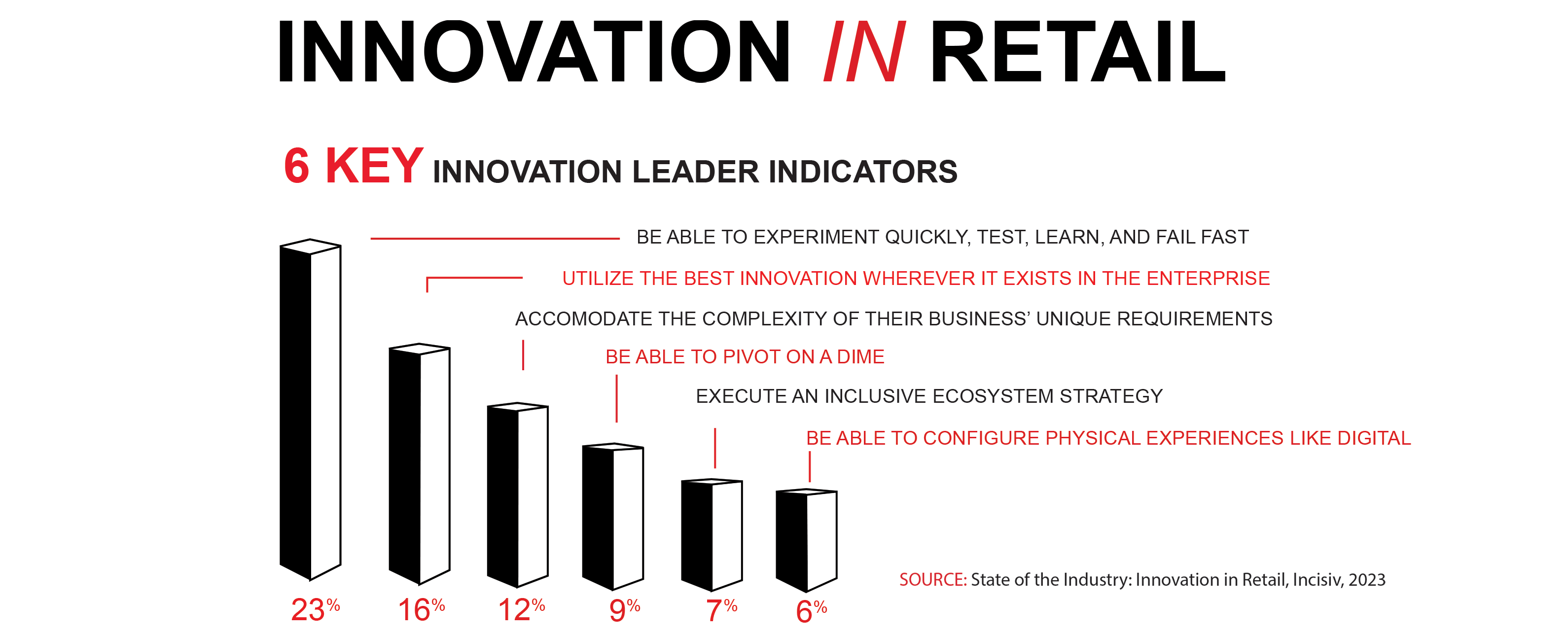
A recent study conducted by Incisiv and Toshiba, "State of the Industry: Innovation in Retail," identified six key innovation capabilities:
• Be able to experiment quickly
• Utilize the best innovation wherever it exists in the enterprise
• Accommodate the complexity of your business
• Be able to pivot rapidly
• Execute an inclusive ecosystem strategy
• Be able to configure physical experiences like digital ones
Of those surveyed, only 17% are classified as innovation leaders, and then nearly a quarter of that 17% were deficient in all categories except in quick experimentation. That means innovation leadership is currently focused on having the ability to experiment quickly.
Experiment Quickly
Rapid experimentation aims to try things as quickly and efficiently as possible to reduce the risk of investing time and resources into developing a product or service that may fail to be successful in the market. By rapidly testing different ideas and gathering customer feedback, retailers can adjust their strategies and make improvements based on real-time data. When retailers have the freedom to experiment at the speed of their business, they also have the freedom to fail fast and move onto finding other solutions worth their time, money, and efforts.
Utilize Innovation
In addition to being able to experiment quickly, a true innovative retailer takes advantage of the best innovation wherever it exists in the company. A significant example of this is using eCommerce personalization in-store. Tailoring the shopping experience to the needs of the individual customer means retailers can increase engagement, loyalty, and sales taking an existing approach they are familiar with and having a new way to apply it that they had not done before. Personalization can also improve the customer experience by making it easier for customers to find what they're looking for and providing more relevant and helpful information throughout the shopping process.
Accommodate Complexity
Every company has its own set of complex customizations within its organization, and to be successful, retailers should accommodate these complexities. One such complexity is off-catalog returns. These can pose a challenge for retailers, as they may not have a clear record of the product or its sale. To manage these returns, retailers need to implement a management system to help track and manage all returns, including off-catalog returns. These systems can help retailers streamline the return process, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Pivot Easily
Retailers may pivot their business in response to various factors, such as shifts in shopper preferences, changes in the competitive landscape, or the impact of new innovations. For example, when a retailer shifts its focus from physical stores to eCommerce. In recent years, many traditional brick-and-mortar retailers have pivoted to digital channels to meet the growing demand for online shopping. Unexpected demand, supply chain blockages, supplier mix-ups, customer expectations, new technology; all these scenarios are why it's vital for a company's success that a retailer ensures that it's easy to change strategies.
Pivoting can be an essential strategic tool for retailers to stay competitive and adapt to changing market conditions. By adapting their business, retailers can better meet shoppers' evolving needs and preferences and position themselves for long-term growth and success.
Execute an Inclusive Ecosystem
A connected store ecosystem creates a seamless and frictionless retail experience for both the shopper and the retailer. This connectivity improves efficiency, data accuracy, and operational performance. But what does an inclusive ecosystem strategy look like?
• Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems – used to process transactions, manage inventory, and
generate sales reports
• Supply Chain Management Systems – Helps retailers manage inventory, track
shipments, and optimize supply chain operations
• Consumer Shopping Apps – Aids in customer interactions and preferences and use
that data to provide personalized shopping experiences
• Commerce Platforms – Creates a unified customer experience, improves store
operations, and increases overall productivity by combining technologies throughout a business.
Combine Physical & Digital
An innovative retail strategy includes both online and in-store experiences for shoppers. Shoppers want to move between touchpoints – digital and physical – seamlessly. In response, retailers need to knock down the walls that separate their channels, enabling shoppers to easily move from online to store, to mobile, to home delivery, and beyond.
Finding innovative ways to combine a digital and physical strategy opens several opportunities for retailers, including personalization, flexibility, and enhancing physical stores with digital solutions.
Overall, it is critical for organizations to continuously innovate to remain relevant and meet the changing needs of their customers.
A culture that encourages and awards experimentation, risk-taking, and collaboration is the key to successful innovation. This requires leaders willing to embrace change and invest in innovation initiatives that can drive growth and transform the organization.







